Observation and Measurement of Nanofibres Using Digital Microscopes
Nanofibres are extremely fine fibres with a diameter less than 100 nm. Reducing the fibre size to nanometres provides new functions such as antimicrobial properties, ultrafine particle trapping performance, and the slip flow effect (higher breathability). This section introduces examples of observation of nanofibres using a digital microscope.

- Nanofibre Definition
- Nanofibre Materials and Types
- Effects of Nanofibres
- What is Cellulose Nanofibre (CNF)?
- Nanofibre Observation Examples Using Digital Microscopes
Nanofibre Definition
Nanofibres are defined as fibrous materials with a diameter from 1 nm to 100 nm and a length of 100 times or more the diameter.
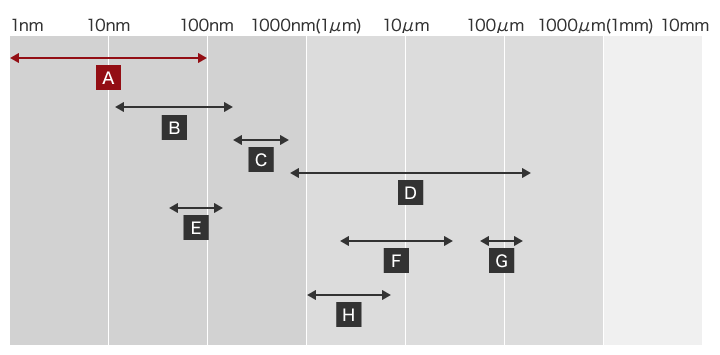
- A: Nanofibre
- B: Ultraviolet
- C: Visible light
- D: Infrared
- E: Virus
- F: Bacteria
- G: Hair root
- H: Microfibre
Nanofibre Materials and Types
Nanofibres come in various types that can be classified according to the material. A variety of applications make use of their different properties.
Major nanofibre types
| Type | Material |
|---|---|
| Polymeric nanofibre |
Polypropylene, polyethylene terephthalate |
| Bionanofibre |
Cellulose, chitin |
| Carbon nanofibre |
Carbon nanotube |
| Metal nanofibre |
Metal (iron, aluminium, copper, nickel, silver, etc.) |
| Ceramic nanofibre |
Silica |
Effects of Nanofibres
- High-performance filters with low pressure losses can be manufactured due to the slip flow effect.
- Large specific surface areas provide high adsorption performance.
- High sound absorption effect and thermal insulation effect
- Nanofibres are light but strong, which allow them to be used in place of metal materials.
What is Cellulose Nanofibre (CNF)?
Cellulose nanofibres (CNFs) are biomass produced by reducing the size of cellulose, derived from plant fibres, to nano-order size which is several hundred times smaller than a micrometre. CNFs are characterised by low environmental load caused by manufacturing and disposal because they are derived from plant. They also offer light weight, high strength, and high anti-expansion properties and are used for a wide range of products including automobiles, home appliances, and building materials.
Nanofibre Observation Examples Using Digital Microscopes
These are the latest examples of observation of nanofibres using KEYENCE’s VHX Series 4K Digital Microscope.
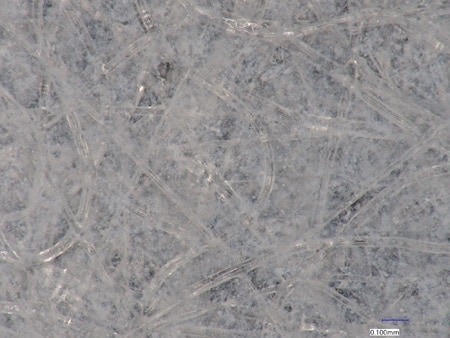
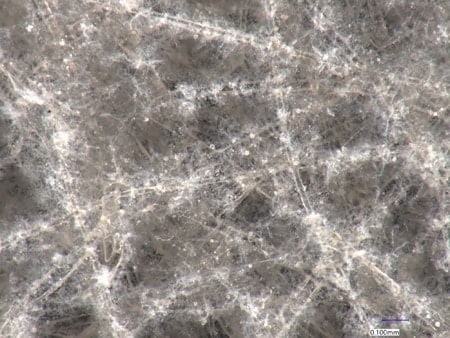
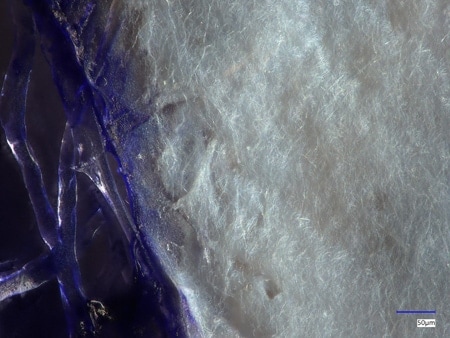
Colours can be evaluated, which is difficult with SEMs.

VH-Z500, 2000×, coaxial illumination
Left: With depth composition Right: Without depth composition
The depth composition function allows for in-focus observation of even deep fibres.