CODE 128 and GS1-128
About 100 types of barcodes are available in the world. The following is an introduction to CODE128 and GS1-128 barcodes.
CODE 128
CODE 128 is the barcode developed by Computer Identics Corporation (U.S.A.) in 1981.
CODE 128 can represent all 128 ASCII code characters (numbers, upper case/lower case letters, symbols and control codes). Since it can represent all characters (except Japanese kanji, hiragana and katakana) that can be used with a computer keyboard, it is a computer friendly barcode.
CODE 128 Composition
The basic composition is as follows:

- A
- Start code
- B
- Check digit (Modulus 103)
- C
- Stop code
- There are 4 types of bar size.
- One character is represented by 3 bars and 3 spaces (total six elements).
- A start character has three types; "CODE-A", "CODE-B" and "CODE-C". The type of start character determines the character composition of subsequent characters. (See here for the table of character composition. For example, when CODE A is used as a start character, the characters in the CODE-A column can be represented.)

- A
- Start with CODE-C
- B
- Change to CODE-A
- When CODE-C is used, 2-digits numbers can be represented by one type of bar pattern. This allows the very high data density.
- When code set characters (CODE-A, CODE-B and CODE-C) are used, the barcode started with the start character of CODE-A can be changed to use the characters in the CODE-B or CODE-C column in the middle of barcode processing.
- When "SHIFT" is used, only one character next to the SHIFT can be changed to the character in the next column (A to B, B to C, C to A). (Similar to the SHIFT key operation of on the computer keyboard)
- "Modulus 103" is used as a check digit.
CODE 128 Character Composition
| Numerical value |
CODE A |
CODE B |
CODE C |
Bar pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | SP | SP | 00 |  |
| 1 | ! | ! | 01 |  |
| 2 | " | " | 02 |  |
| 3 | # | # | 03 |  |
| 4 | $ | $ | 04 |  |
| 5 | % | % | 05 |  |
| 6 | & | & | 06 |  |
| 7 | ' | ' | 07 |  |
| 8 | ( | ( | 08 |  |
| 9 | ) | ) | 09 |  |
| 10 | * | * | 10 |  |
| 11 | + | + | 11 |  |
| 12 | , | , | 12 |  |
| 13 | - | - | 13 |  |
| 14 | . | . | 14 |  |
| 15 | / | / | 15 |  |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 16 |  |
| 17 | 1 | 1 | 17 |  |
| 18 | 2 | 2 | 18 |  |
| 19 | 3 | 3 | 19 |  |
| 20 | 4 | 4 | 20 |  |
| 21 | 5 | 5 | 21 |  |
| 22 | 6 | 6 | 22 |  |
| 23 | 7 | 7 | 23 |  |
| 24 | 8 | 8 | 24 |  |
| 25 | 9 | 9 | 25 | 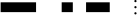 |
| 26 | : | : | 26 |  |
| 27 | ; | ; | 27 |  |
| 28 | < | < | 28 |  |
| 29 | = | = | 29 |  |
| 30 | > | > | 30 |  |
| 31 | ? | ? | 31 |  |
| 32 | @ | @ | 32 |  |
| 33 | A | A | 33 |  |
| 34 | B | B | 34 |  |
| 35 | C | C | 35 |  |
| 36 | D | D | 36 |  |
| 37 | E | E | 37 |  |
| 38 | F | F | 38 |  |
| 39 | G | G | 39 |  |
| 40 | H | H | 40 |  |
| 41 | I | I | 41 |  |
| 42 | J | J | 42 |  |
| 43 | K | K | 43 |  |
| 44 | L | L | 44 |  |
| 45 | M | M | 45 | 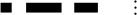 |
| 46 | N | N | 46 |  |
| 47 | O | O | 47 |  |
| 48 | P | P | 48 |  |
| 49 | Q | Q | 49 |  |
| 50 | R | R | 50 |  |
| 51 | S | S | 51 |  |
| 52 | T | T | 52 |  |
| 53 | U | U | 53 |  |
| 54 | V | V | 54 |  |
| 55 | W | W | 55 |  |
| 56 | X | X | 56 |  |
| 57 | Y | Y | 57 |  |
| 58 | Z | Z | 58 |  |
| 59 | [ | [ | 59 |  |
| 60 | \ | \ | 60 |  |
| 61 | ] | ] | 61 |  |
| 62 | ^ | ^ | 62 |  |
| 63 | _ | _ | 63 |  |
| 64 | NUL | ` | 64 |  |
| 65 | SOH | a | 65 |  |
| 66 | STX | b | 66 |  |
| 67 | ETX | c | 67 |  |
| 68 | EOT | d | 68 |  |
| 69 | ENQ | e | 69 |  |
| 70 | ACK | f | 70 |  |
| 71 | BEL | g | 71 |  |
| 72 | BS | h | 72 |  |
| 73 | HT | i | 73 |  |
| 74 | LF | j | 74 |  |
| 75 | VT | k | 75 |  |
| 76 | FF | l | 76 | 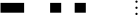 |
| 77 | CR | m | 77 |  |
| 78 | SO | n | 78 |  |
| 79 | SI | o | 79 |  |
| 80 | DLE | p | 80 |  |
| 81 | DC1 | q | 81 |  |
| 82 | DC2 | r | 82 |  |
| 83 | DC3 | s | 83 |  |
| 84 | DC4 | t | 84 |  |
| 85 | NAK | u | 85 |  |
| 86 | SYN | v | 86 |  |
| 87 | ETB | w | 87 |  |
| 88 | CAN | x | 88 |  |
| 89 | EM | y | 89 | 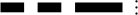 |
| 90 | SUB | z | 90 |  |
| 91 | ESC | { | 91 |  |
| 92 | FS | | | 92 |  |
| 93 | GS | } | 93 |  |
| 94 | RS | ~ | 94 |  |
| 95 | US | DEL | 95 |  |
| 96 | FNC 3 | FNC 3 | 96 |  |
| 97 | FNC 2 | FNC 2 | 97 |  |
| 98 | SHIFT | SHIFT | 98 |  |
| 99 | CODE C | CODE C | 99 |  |
| 100 | CODE B | FNC 4 | CODE B |  |
| 101 | FNC 4 | CODE A | CODE A |  |
| 102 | FNC 1 | FNC 1 | FNC 1 |  |
| 103 | START (CODE A) |  |
||
| 104 | START (CODE B) |  |
||
| 105 | START (CODE C) |  |
||
| STOP |  |
|||
CODE 128 Features
- CODE 128 barcode can include all 128 ASCII code characters (including control codes such as [ESC], [STX], [ETX], [CR] and [LF]).
- When CODE-C is used as the start character, one bar pattern can represent 2-digits numbers. This allows very efficient barcode composition. If the barcode data has 12 or more digits, CODE 128 provides smaller size than ITF.
- Since CODE 128 uses 4 types of bar size, printers with high print quality are required. CODE 128 is not suitable for printing with dot matrix printers and FA ink-jet printers and for flexographic printing on corrugated cardboards.
CODE 128 Applications
Use of CODE-C as the start code allows CODE 128 to provide the barcode with very high data density, if only numbers are handled.
GS1-128 makes use of the characteristics of CODE 128 and is currently used in many industrial applications. With GS1-128, various data are included in the barcode, such as manufacturing date of the product, open date, weight, size, lot number, destination, customer's account, etc.
CODE 128 is used in the following industries:
- U.S.A. apparel industry
- U.S.A. food process industry
- U.S.A. drugs and medical equipment industry
- Food industries in Australia and New Zealand
- European drugs and medical instruments industry
GS1-128
What Is GS1-128?
GS1-128 is the barcode that provides various data including distribution and business transaction data in addition to the data provided by the JAN code and the standard distribution code (ITF) currently available.
Following data can be included in GS1-128 barcode:
- Package number
- Quantity in package
- Weight, capacity and cubic capacity
- Manufacturing date and validity of quality
- Lot number
- Location number (destination)
- Customer's account code
- Customer's order number
Necessary data is used to form the barcode label for the various applications.
For example, On-line purchasing/ordering using EDI (the system for exchanging electronic data between companies), management of open date for foods, management of drugs validity, simplifying the work for checking incoming products, sorting packages for every destination, etc.(The following label is a sample from a food manufacturer.)

- A
- Product item code
- B
- Validity of quality (August 27, 1999)
- C
- Delivery quantity
- D
- Net weight
- E
- Lot number
- F
- Serial number
Background of GS1-128 Establishment
JAN code and the standard distribution code (ITF) are the barcodes for indicating the product itself and its quantity and not for the data such as manufacturing date, package number, validity of quality and order number.
While CODE 39 allows such data to be included in the barcode, the exchange of such data between companies is not allowed because the definition and the number of digits of the data are different.
GS1-128 is established as the world universal barcode for common use, with the items and the number of digits of the data and the type of the barcode being standardised.
GS1-128 Composition
The basic composition of GS1-128 is as follows:
- Code 128 is used as the barcode.
- In order to separate the required data such as weight and open data, the "application identifier (AI)" is added which is followed by the data. If more than one data is represented, each data shall be linked.

- A
- A.I. to indicate delivery container code
- B
- A.I. to indicate validity of quality
- C
- A.I. to indicate delivery quantity
Although application identifiers are parenthesised, the parentheses are not included in the barcode data. They are used just for presentation.
In the sample above, following the application identifier "01", 14-digits code is assigned to identify the delivery container (minimum package unit for corrugated cardboard boxes). Following the application identifier "15", the data representing the validity of quality (consumption validity or drug validity) is given to show August 27, '95. Following the last application identifier "30", the data representing the delivery quantity is given to show 3 pieces.
There are about 100 application identifiers except the above. The required data is selected and included in the barcodes by users.
GS1-128 is not intended to represent fixed data, but the data is selectable by the user. Therefore, for consistent use of GS1-128 among companies, the standards for the barcode system with the data available shall be prepared by the respective industry and the groups of companies involved.
- In order to distinguish GS1-128 from CODE 128, it is required to give [FNC 1](function 1) following the start code (CODE-A to C).
- Even if the number of digits for the data following the application identifier is a variable-length, [FNC 1] is given to separate the data.
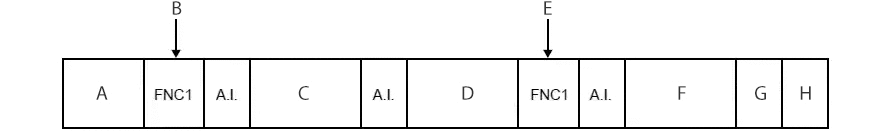
- A
- Start code C
- B
- [FNC 1] to signal GS1-128
- C
- Data 1 (fixed-length)
- D
- Data 2 (variable-length)
- E
- [FNC 1] to separate the data
- F
- Data 3 (variable-length)
- G
- Check digit
- H
- Stop code
- With GS1-128 being added to EAN code and the standard distribution code (ITF), it can be used as the code to add more data.
GS1-128 is designed to represent the application identifiers and the products relative data or the transaction data of the companies using CODE 128.
In other words, GS1-128 is the standard for the applications to represent the various data. CODE 128 is the standard just for the barcode itself. The difference between GS1-128 and CODE 128 is whether it represents the application or not.
Since GS1-128 uses the barcode composition of CODE 128, any barcode reader that can read CODE 128 can be used to read the GS1-128 data.
Application Identifier
Application Identifier
There are 100 types of application identifiers that can be classified as follows. Some of the data following each application identifier has a fixed number of digits (standard carton ID, date and unit of measurement), while the others have an undefined number of digits (lot number, serial number, quantity in package, quantity and order number).
| Classification | Content | Application identifier |
|---|---|---|
| Package style |
|
00 "Standard carton ID" |
| Products management |
|
01 "Delivery container code" |
|
20 | |
|
11~17 | |
|
10 | |
|
21 | |
| Measurement indication |
|
310~369 |
| Administration |
|
400 |
|
401 | |
|
410~421 | |
|
90~99 |
Typical application identifiers
| Application identifier | Content | Data's number of digits |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | Standard carton ID | Numbers with 18 digits |
"00" is the identifier that gives the package serial number to every corrugated cardboard box and pallet for delivery. Therefore, a different number is given for every delivery.
The data has 18 digits with the following composition:
| Package type | 1 digit |
| Universal company code | 7 digits |
| Package serial number for every delivery | 9 digits |
| Check digit (modulus 10/3 weight) | 1 digit |
"Package type" is as follows:
| Package type | |
|---|---|
| 0 | Case or carton |
| 1 | Pallet (larger than case and carton) |
| 2 | Container (larger than pallet) |
| 3 | Any package type other than above |
| 4 | According to internal requirements (for internal use) |
| 5 | According to mutual requirements among the companies concerned |
| 6~9 | No use allowed |
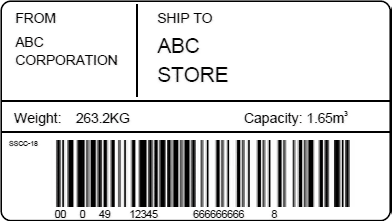
"Universal company code" is indicated by "country code" + "manufacturer code" for the companies who registered JAN. For the companies who did not register JAN, it is required to obtain the universal business account code.
"Standard carton ID" is called SSCC-18 (Serial Shipping Container Code) in Europe and America.
| Application identifier | Content | Data's number of digits |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | Delivery container code | Numbers with 14 digits |
The same composition of the standard distribution code (ITF) is generally applied to "01". It consists of the EAN code of the packaged product and the package indicator that indicates the product quantity.
| Package indicator | 1 digit |
| EAN code | 12 digits |
| Check digit (Modulus 10/3 weight) | 1 digit |
"Package indicator" is as follows:
| Package indicator | |
|---|---|
| 0 | Corrugated cardboard boxes that contain the mixed products |
| 1~8 | Corrugated cardboard box for one-item that contains the same quantity. Setting within the range of 1 to 8. In many cases, 1 is set. |
| 9 | The corrugated cardboard box that contains the different quantity for one-item |
Since "delivery container code" has the same data composition as for the EAN code and the standard distribution code, it can be used only on the condition that EAN and standard distribution codes are not printed on corrugated cardboard boxes.
"Delivery container code" is called SCC-14 (Shipping Container Code) in Europe and America.
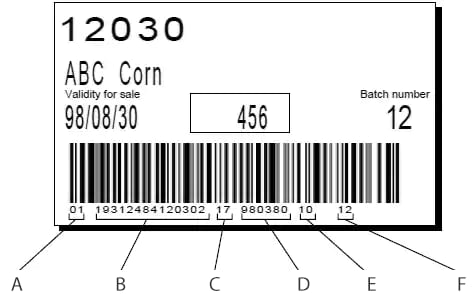
- A
- Identifier (01 is the delivery container code.)
- B
- Delivery container code
- C
- Identifier (17 represents the validity for sale.)
- D
- Validity for sale (August 30, ’98)
- E
- Identifier (10 is the batch number.)
- F
- Batch number
| Application identifier | Content | Format |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | Batch number or lot number | Within 20 alphanumeric characters |
"10" is the application identifier to indicate the batch number and the lot number of the product. 20 alphanumeric characters (variable-length) or less are available.
| Application identifier | Content | Format |
|---|---|---|
| 11 | Manufacturing date (YYMMDD) | Numbers with 6 digits |
| 13 | Packaged date (YYMMDD) | Numbers with 6 digits |
| 15 | Validity of quality (YYMMDD) | Numbers with 6 digits |
| 17 | Validity for sale (YYMMDD) | Numbers with 6 digits |
The data of various dates are indicated.
For the validity of quality, the important data necessary for management are indicated. For example, "open date" of foods and "drugs validity" of drugs.
| Application identifier | Content | Format |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | Administration number (customer's order number) | Within 30 alphanumeric characters |
| 411 | Location number (customer's account code) | Numbers with 13 digits |
These are the application identifiers to indicate the administration data such as "order number" of customers and "customer's account code".
| Application identifier | Content | Format |
|---|---|---|
| 410 | Location number (destination code) | Numbers with 13 digits |
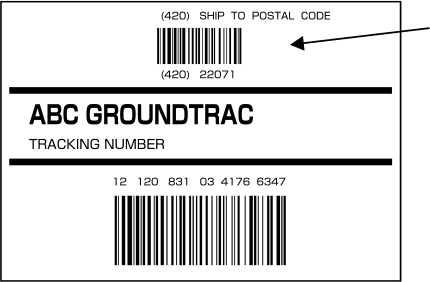
| 420 | Location number (destination postal code) | Within 9 alphanumeric characters |
They are used for sorting goods according to destinations. "410" is the application identifier that allows the sorting for every company with EAN company codes being used.
"420" is the application identifier that allows the sorting for every delivery destination with postal numbers being used.