What is a QR code?
Structure of QR Codes
QR code (Quick response code) is a matrix 2D code for high-speed reading developed by DENSO WAVE in 1994. It was registered to the ITS standard of the AIMI in 1997 and to ISO/IEC standards in 2000.
In addition, Micro QR code was standardised as JIS-X-0510 in 2004.
Specifications of QR Codes
The smallest element (black or white square) of the QR code is called “a module”. A QR code is composed of a combination of black and white modules, position detection patterns, timing patterns,
format information that contains error correction level and mask numbers, data area and error correction code
(Reed-Solomon code).
| Specifications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smallest symbol size | 21 x 21 modules | |
| Largest symbol size | 177 x 177 modules | |
| Maximum data capacity | Numeric | 7089 characters |
| Alphanumeric | 4296 characters | |
| Kanji | 1817 characters | |
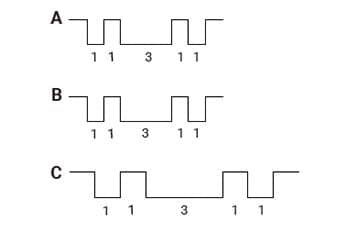
Position detection patterns
The position detection patterns are arranged at three corners of the QR codes. (Micro QR has one.) The position of QR code is detected with the position detection patterns that allow high-speed reading.
From any position of A, B and C, the rate of black and white modules is 1:1:3:1:1 to specify the rotation angle/ displacement of the code.
It can be read from any direction, which significantly improves work efficiency.


Alignment pattern
The alignment pattern is used for position detection when there is displacement of modules due to distortion.
It is applied to model 2.

- A
- Alignment pattern
Margin
The margin is a blank area around the QR code. Model 1 and 2 require a margin of four modules and Micro QR code requires of two modules.

- A
- Margin
Timing pattern
White and black modules are alternately arranged to determine the coordinate.

- A
- Timing pattern
Format information
It contains the error correction rate and mask pattern of the code. The format information is read first when the code is decoded.

- A
- Format information
Error-correcting code (Reed-Solomon code)
Reed-Solomon code is applied to restore the data when a part of QR code is missing or damaged. The restoration rate varies on 4 different error correcting levels.



| Error correcting level | Damaged area to entire code size |
|---|---|
| L | 7% |
| M | 15% |
| Q | 25% |
| H | 30% |
Arrangement of error-correcting code
Data and error correcting code are arranged as shown below. (Sample: Version 2 of Model 2 with level M) A mask is applied to the code to prevent the same pattern with the position detection pattern from appearing.

- A
- Data (D1-)
- B
- Error correcting code (E1-)
Specifications of QR Codes
QR codes are classified into Model 1, Model 2 and Micro QR. They have different features and data capacities.
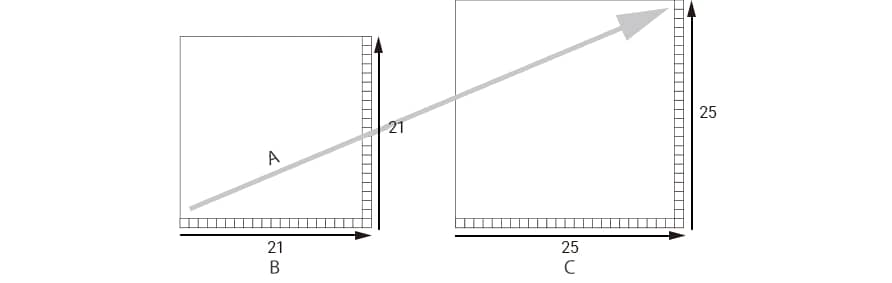
“Version” indicates the size (number of modules) of a QR code. A larger version contains greater data. (The actual size of the code increases as well.)
The standard version is 21 x 21 modules (MicroQR has 11 x 11 modules), and as version increases, 4 modules (2 modules for MicroQR) are added on each side.
Model 1

Model 1 is the prototype of Model 2 and Micro QR. 1 to 14 versions are registered to the AIMI standard.
| Maximum data capacity | |
|---|---|
| Numeric | 1167 characters |
| Alphanumeric | 707 characters |
| Binary | 468 bytes |
| Kanji | 299 characters |
When a version increases, 4 modules are added to the code in both the X and Y directions.
Model 2

- A
- Alignment pattern
Model 2 has an alignment pattern for better position adjustment and contains greater data than Model 1. 1 to 40 versions are registered to the AIMI standard. The version 40 can contain up to 7089 numeric characters.
| Maximum data capacity | |
|---|---|
| Numeric | 7089 characters |
| Alphanumeric | 4296 characters |
| Binary | 2953 bytes |
| Kanji | 1817 characters |
When a version increases, 4 modules are added to the code in both the X and Y directions.
- A
- Data increase
- B
- Version 1
- C
- Version 2
Micro QR
Micro QR has only one position detection pattern to reduce the size so that it can be printed on minute components such as printed circuit boards. The least numbers of modules are 11 x 11.
Micro QR codes offer a space-saving alternative to linear barcodes for applications where 35 characters or less are acceptable.

- A
- Data increase
- B
- Version 1
- C
- Version 2
| Maximum data capacity | |
|---|---|
| Numeric | 35 characters |
| Alphanumeric | 21 characters |
| Binary | 15 bytes |
| Kanji | 9 characters |
When a version increases, 2 modules are added to the code in both the X and Y directions.
How to determine the QR code size
The size of QR code is determined by the version and the size of a module.
(1) Determine the version
Select a version according to data contents, character type and error correction rate.
See below for maximum number of input characters.
(2) Determine the module size
Determine the module size considering the resolution of the printer, and the performance of the scanner.
(3) The QR code size is determined
The actual size of QR code is determined by multiplying the number of modules by the printable size of module. Add margins to determine the required space for the QR code. Model 1 and 2 require 4 modules and MicroQR requires 2 modules as margin on each side.
When the module size is 0.25 mm,
- the sizes of QR code are:
- 5.25 x 5.25 mm for version 1 (21 x 21)
- 8.25 x 8.25 mm for version 4 (33 x 33)
- required spaces including margins are:
- 7.25 x 7.25 mm for version 1 (29 x 29)
- 10.25 x 10.25 mm for version 4 (41 x 41)
Data capacity of each version
Model 2
| Version (module numbers) | Numeric | Alphanumeric | Binary | Kanji | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | M | Q | H | L | M | Q | H | L | M | Q | H | L | M | Q | H | |
| 1 (21) | 41 | 34 | 27 | 17 | 25 | 20 | 16 | 10 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 7 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 4 |
| 2 (25) | 77 | 63 | 48 | 34 | 47 | 38 | 29 | 20 | 32 | 26 | 20 | 14 | 20 | 16 | 12 | 8 |
| 3 (29) | 127 | 101 | 77 | 58 | 77 | 61 | 47 | 35 | 53 | 42 | 32 | 24 | 32 | 26 | 20 | 15 |
| 4 (33) | 187 | 149 | 111 | 82 | 114 | 90 | 67 | 50 | 78 | 62 | 46 | 34 | 48 | 38 | 28 | 21 |
| 5 (37) | 255 | 202 | 144 | 106 | 154 | 122 | 87 | 64 | 106 | 84 | 60 | 44 | 65 | 52 | 37 | 27 |
| 6 (41) | 322 | 255 | 178 | 139 | 195 | 154 | 108 | 84 | 134 | 106 | 74 | 58 | 82 | 65 | 45 | 36 |
| 7 (45) | 370 | 293 | 207 | 154 | 224 | 178 | 125 | 93 | 154 | 122 | 86 | 64 | 95 | 75 | 53 | 39 |
| 8 (49) | 461 | 365 | 259 | 202 | 279 | 221 | 157 | 122 | 192 | 152 | 108 | 84 | 118 | 93 | 66 | 52 |
| 9 (53) | 552 | 432 | 312 | 235 | 335 | 262 | 189 | 143 | 230 | 180 | 130 | 98 | 141 | 111 | 80 | 60 |
| 10 (57) | 652 | 513 | 364 | 288 | 395 | 311 | 221 | 174 | 271 | 213 | 151 | 119 | 167 | 131 | 93 | 74 |
| 11 (61) | 772 | 604 | 427 | 331 | 468 | 366 | 259 | 200 | 321 | 251 | 177 | 137 | 198 | 155 | 109 | 85 |
| 12 (65) | 883 | 691 | 489 | 374 | 535 | 419 | 296 | 227 | 367 | 287 | 203 | 155 | 226 | 177 | 125 | 96 |
| 13 (69) | 1022 | 796 | 580 | 427 | 619 | 483 | 352 | 259 | 425 | 331 | 241 | 177 | 262 | 204 | 149 | 109 |
| 14 (73) | 1101 | 871 | 621 | 468 | 667 | 528 | 376 | 283 | 458 | 362 | 258 | 194 | 282 | 223 | 159 | 120 |
| 15 (77) | 1250 | 991 | 703 | 530 | 758 | 600 | 426 | 321 | 520 | 412 | 292 | 220 | 320 | 254 | 180 | 136 |
| 16 (81) | 1408 | 1082 | 775 | 602 | 854 | 656 | 470 | 365 | 586 | 450 | 322 | 250 | 361 | 277 | 198 | 154 |
| 17 (85) | 1548 | 1212 | 876 | 674 | 938 | 734 | 531 | 408 | 644 | 504 | 364 | 280 | 397 | 310 | 224 | 173 |
| 18 (89) | 1725 | 1346 | 948 | 746 | 1046 | 816 | 574 | 452 | 718 | 560 | 394 | 310 | 442 | 345 | 243 | 191 |
| 19 (93) | 1903 | 1500 | 1063 | 813 | 1153 | 909 | 644 | 493 | 792 | 624 | 442 | 338 | 488 | 384 | 272 | 208 |
| 20 (97) | 2061 | 1600 | 1159 | 919 | 1249 | 970 | 702 | 557 | 858 | 666 | 482 | 382 | 528 | 410 | 297 | 235 |
| 21 (101) | 2232 | 1708 | 1224 | 969 | 1352 | 1035 | 742 | 587 | 929 | 711 | 509 | 403 | 572 | 438 | 314 | 248 |
| 22 (105) | 2409 | 1872 | 1358 | 1056 | 1460 | 1134 | 823 | 640 | 1003 | 779 | 565 | 439 | 618 | 480 | 348 | 270 |
Micro QR
| Version | Error correcting | Numeric | Alphanumeric | Binary | Kanji |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 (11) | Error detection | 5 | - | - | - |
| M2 (13) | L | 10 | 6 | - | - |
| M | 8 | 5 | - | - | |
| M3 (15) | L | 23 | 14 | 9 | 6 |
| M | 18 | 11 | 7 | 4 | |
| M4 (17) | L | 35 | 21 | 15 | 9 |
| M | 30 | 18 | 13 | 8 | |
| Q | 21 | 13 | 9 | 5 |


![Basics of 2D codes VOL.1 [Types of 2D codes]](/img/asset/AS_151321_L.jpg)

