CODE 39 and Codabar
About 100 types of barcodes are available in the world. The following is an introduction to CODE39 barcodes.
CODE39
CODE 39 is the barcode developed by Intermec Corporation in 1975. Up to 43 characters including numbers, letters and some symbols can be included in the barcode. Since letters can be handled, CODE 39 is indispensable in the industrial fields and used in industries such as automotive and electronics. It is standardised by AIAG (Automotive Industry Action Group) in U.S.A.
CODE 39 Composition
CODE 39 is named for its pattern of bars and spaces, with 3 out of 9 bars and spaces being wide. The basic composition is as follows:
• One letter (character) is represented by 9 bars and spaces.
• Asterisks (*) are attached to the start and end of the barcode. (start/stop character)
• The space between characters is called an "inter-character gap". Generally, the gap width is as wide as the narrow bar width. (The maximum width is ruled to be 3 to 5.3 times wider than that of the narrow bar.)
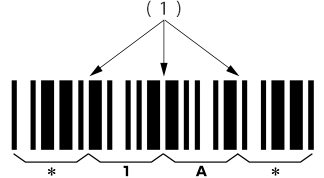
CODE 39 Character Composition
The following table shows the character composition of CODE 39.
CODE 39 can represent characters including numbers (0 to 9), alphabets and symbols (-, ., _ (space), *, $, /, +, %).
| Character | Bar pattern |
|---|---|
| 0 |  |
| 1 |  |
| 2 |  |
| 3 |  |
| 4 |  |
| 5 |  |
| 6 |  |
| 7 |  |
| 8 | 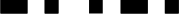 |
| 9 |  |
| A |  |
| B |  |
| C |  |
| D |  |
| E |  |
| F |  |
| G |  |
| H |  |
| I |  |
| J |  |
| K |  |
| L |  |
| M |  |
| N |  |
| O |  |
| P |  |
| Q | 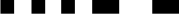 |
| R |  |
| S |  |
| T |  |
| U | 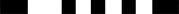 |
| V |  |
| W |  |
| X |  |
| Y |  |
| Z |  |
| - |  |
| . | 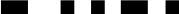 |
| SPACE | 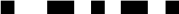 |
| $ | 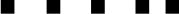 |
| / | 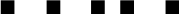 |
| + |  |
| % |  |
| * |  |
CODE 39 Features
- Since CODE 39 represents not only numbers but also letters and symbols, it allows also the item number to be represented.
- The start/stop character is an asterisk (*).
- 9 bars and spaces are used to represent one character. More bars and spaces than other codes provide more complete reading and high reliability, as well as the largest size of barcode.
When the data requires letters, CODE 39 is ideal.
CODE 39 Applications
CODE 39 is used mainly in industrial applications.
Codabar
Codabar is the barcode developed by Monarch Marking Systems in 1972. It is the barcode introduced at early stage following "2 of 5". It is widely used for applications that require serial numbers, such as management of blood banks, slips for door-to-door delivery services and member cards.
Codabar Composition
Codabar has 4 bars and 3 spaces (total 7 elements) with each narrow or wide width representing one character (letter).
The basic composition of Codabar is as follows:
- 7 bars and spaces represent one character.
- Any one of A, B, C or D (a, b, c or d) is attached to the start and end of the barcode.
(start/stop character)

Start/stop character has any combination
of A––––A, B––––B, A––––C, D––––A, etc.
- Inter-character gap is the same as for CODE 39.
Codabar Character Composition
Codabar can represent characters including numbers (0 to 9), letters (A, B, C, D) and symbols (-, $, /, ., +).
| Character | Bar pattern |
|---|---|
| 0 |  |
| 1 |  |
| 2 |  |
| 3 |  |
| 4 |  |
| 5 |  |
| 6 |  |
| 7 |  |
| 8 |  |
| 9 |  |
| - |  |
| $ |  |
| : |  |
| / |  |
| . |  |
| + |  |
| A |  |
| B |  |
| C |  |
| D |  |
Codabar Features
Skip reading is less likely with Codabar than with ITF. Smaller barcode size is possible compared with CODE 39.
However, it does not always mean that skip reading never happens with Codabar. If the print quality of the barcode is poor, skip reading tends to occur as shown below.

If one space is printed wider than what it should be, the character is considered to be a stop character, and the skip reading occurs.
Availability of any start/stop character combination allows versatile usage.
For example, A––––A is used for the list price, A––––C for the special discount price, and C––––C for the price at bargain sale.




