What is a DataMatrix code?
DataMatrix code (ECC200) has two configurations, square and rectangular, and always contains an even number of modules.
- Structure of DataMatrix code
- Structure of DataMatrix codes (ECC200)
- Specifications of DataMatrix code
- GS1 DataMatrix
Structure of DataMatrix code
DataMatrix code is a matrix 2D code that was developed by ID Matrix in 1987. It was registered to the ISS standard of AIMI in 1996 and the ISO/IEC standard in 2000.
| Specifications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Minimum size | 10 x 10 modules | |
| Maximum size | 144 x 144 modules | |
| Maximum data capacity | Numeric | 3116 characters |
| Alphanumeric | 2335 characters | |
Older versions of DataMatrix code include ECC000, ECC050, ECC080, ECC100 and ECC140.
ECC200 is the latest version of DataMatrix code and can be square or rectangular in configuration.
ECC000, ECC050, ECC080, ECC100, ECC140
These are composed of odd-numbered modules from 9 x 9 to 49 x 49 using convolution correction.
Since a slight distortion disturbs reading when the data size is large, the older versions are almost never used.
ECC200
ECC200 has upgraded error correction capacity to eliminate distortion problems.
It uses Reed-Solomon for error correction that restores data when a part of a code is damaged.
ECC200 is internationally standardised. Generally ECC200 version is used when DataMatrix code is required.
Structure of DataMatrix codes (ECC200)
Alignment pattern and clock pattern
The data area of DataMatrix codes is surrounded by an L-shaped frame called the alignment pattern and dotted lines called the clock pattern. Readers capture these patterns to determine the position of the code with image processing. Thus, DataMatrix codes can be read from any direction.
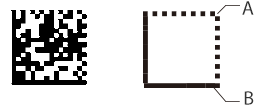
- A
- Clock pattern
- B
- Alignment pattern
When there are more than 24 x 24 modules, the code is divided in blocks that do not exceed 24 modules on a side. This structure prevents distortion of the code.
Code size and number of blocks
There are twenty-four code sizes, ranging from 10 x 10 modules to 144 x 144 modules (including six sizes for the rectangular type).
When a code has more than 26 x 26 modules (more than 24 x 24 modules for data), it is divided in blocks, as seen below, that do not exceed 24 modules on a side. This structure prevents distortion of the code.
| Symbol size | Block | Data cell |
|---|---|---|
| 10x10 to 26x26 | 1 | 8x8 to 24x24 |
| 28x28 to 52x52 | 4 | 14x14 to 24x24 |
| 64x64 to 104x104 | 16 | 14x14 to 24x24 |
| 120x120 to 144x144 | 36 | 18x18 to 22x22 |

Margin
The margin around a DataMatrix code should be larger than a module.

- A
- Margin
Error correcting code (Reed-Solomon code)
The Reed-Solomon code restores the data when a part of the DataMatrix code is damaged.
Arrangement of data and error correcting code
Data and error correcting codes are arranged as shown below.

For converting “YSK” into a DataMatrix code: YSK are coded and error correcting codes are calculated as below and arranged in a square.
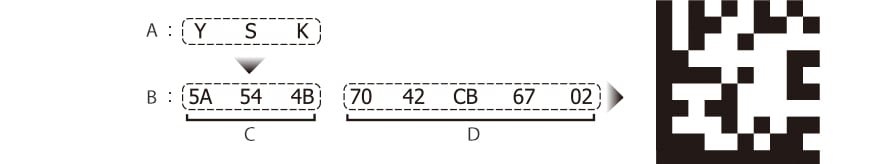
- A
- Original data
- B
- Code (hex)
- C
- Coded data
- D
- Error correcting code
Specifications of DataMatrix code
DataMatrix code (ECC200) has two configurations, square and rectangular, and always contains an even number of cells.
Square type

| Specifications for square type DataMatrix (ECC200) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Minimum size | 10 x 10 modules | |
| Maximum size | 144 x 144 modules | |
| Maximum data capacity | Numeric | 3116 characters |
| Alphanumeric | 2335 characters | |
| Binary | 1556 characters | |
There are twenty-four symbol sizes ranging from 10 x 10 modules to 144 x 144 modules. When there are more than 24 x 24 modules, the code is divided in blocks that do not exceed 24 modules on a side. This structure prevents distortion of the code.
Rectangular type

| Specifications for Rectangular type DataMatrix (ECC200) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Minimum size | 8 x 16 modules | |
| Maximum size | 16 x 48 modules | |
| Maximum data capacity | Numeric | 98 characters |
| Alphanumeric | 72 characters | |
| Binary | 47 characters | |
There are following six sizes for a rectangular type.
- 8 x 18 modules (1 block)
- 12 x 26 modules (1 block)
- 16 x 36 modules (1 block)
- 8 x 32 modules (2 blocks)
- 12 x 36 modules (2 blocks)
- 16 x 48 modules (2 blocks)
How to determine the DataMatrix code size
The actual size of the DataMatrix code is determined by multiplying the symbol size by the printable size of the module.
When the size of the module is 0.25 mm,
Symbol size: 10 x 10 modules = 2.5 x 2.5 mm
Symbol size: 32 x 32 modules = 8.0 x 8.0 mm
Symbol size: 8 x 18 modules = 2.0 x 4.5 mm
Data capacity of each symbol size
Square type
| Module numbers | Data capacity | Error correcting rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numeric | Alphanumeric | Binary | ||
| 10 x 10 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 25% |
| 12 x 12 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 25% |
| 14 x 14 | 16 | 10 | 6 | 28 to 39% |
| 16 x 16 | 24 | 16 | 10 | 25 to 38% |
| 18 x 18 | 36 | 25 | 16 | 22 to 34% |
| 20 x 20 | 44 | 31 | 20 | 23 to 38% |
| 22 x 22 | 60 | 43 | 28 | 20 to 34% |
| 24 x 24 | 72 | 52 | 34 | 20 to 35% |
| 26 x 26 | 88 | 64 | 42 | 19 to 35% |
| 32 x 32 | 124 | 91 | 60 | 18 to 34% |
| 36 x 36 | 172 | 127 | 84 | 16 to 30% |
| 40 x 40 | 228 | 169 | 112 | 15 to 28% |
| 44 x 44 | 288 | 214 | 142 | 14 to 27% |
| 48 x 48 | 348 | 259 | 172 | 14 to 27% |
| 52 x 52 | 408 | 304 | 202 | 15 to 27% |
| 64 x 64 | 560 | 418 | 278 | 14 to 27% |
| 72 x 72 | 736 | 550 | 366 | 14 to 26% |
| 80 x 80 | 912 | 682 | 454 | 15 to 28% |
| 88 x 88 | 1152 | 862 | 574 | 14 to 27% |
| 96 x 96 | 1392 | 1042 | 694 | 14 to 27% |
| 104 x 104 | 1632 | 1222 | 814 | 15 to 28% |
| 120 x 120 | 2100 | 1573 | 1048 | 14 to 27% |
| 132 x 132 | 2608 | 1954 | 1302 | 14 to 26% |
| 144 x 144 | 3116 | 2335 | 1556 | 14 to 27% |
Rectangular type
| Module numbers | Data capacity | Error correcting rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numeric | Alphanumeric | Binary | ||
| 8 x 18 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 25% |
| 8 x 32 | 20 | 13 | 8 | 24% |
| 12 x 26 | 32 | 22 | 14 | 23 to 37% |
| 12 x 36 | 44 | 31 | 20 | 23 to 38% |
| 16 x 36 | 64 | 46 | 30 | 21 to 38% |
| 16 x 48 | 98 | 72 | 47 | 18 to 33% |
GS1 DataMatrix
GS1 DataMatrix is a 2D code symbol that was standardised by GS1 for distribution. It is based on the ECC200 Standard and defines the following rules in order to differentiate from conventional DataMatrix code.
Major contents of GS1 DataMatrix code
| Code used | DataMatrix ECC200 |
|---|---|
| FNC1 | [FNC1] is placed at the top of the data in order to define it as GS1's standard specifications. |
| Application identifier (AI) | An identifying code that is added to the beginning of the data strip to define what kind of information follows this identifying code. Application identifiers (AI) are specified by ISO/IEC. |
| Variable length data | When entering data in which the amount of information changes (variable length data) such as a quantity, insert [FNC1] as a separator after the variable-length data. This [FNC1] is specified to output [GS] (1Dh in ASCII code) when read by a code reader. * [GS]: Group separator |
Print size for a GS1 module
GS1 recommends the following sizes for a module when printing GS1 DataMatrix code.
| Recommended module size | Maximum module size | Minimum module size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Printing on a label | 0.300 mm | 0.615 mm | 0.255 mm |
| DPM | 0.380 mm | 0.495 mm | 0.380 mm |
Sample of GS1 DataMatrix code

| Element | AI | Data |
|---|---|---|
| GTIN (14 fixed digits) | 01 | 04912345678904 |
| Quantity (variable length) | 30 | 100 |
| Sell-by date | 17 | 120401 |
Relation to GS1-128
GS1 DataMatrix code has the same data structure as that of GS1-128. Thus, it likely will be used when it is necessary to deal with large amounts of data despite the fact that print area is limited. In addition, GS1 DataMatrix code will be standardised in the medical industry. Since codes are to be directly printed on steel medical instruments, such as surgical knifes and scissors, the guidelines have been established.
Steel medical instrument: An instrument that is produced with such materials as stainless, aluminium, copper alloy, titanium, or ceramics, and is reused in medical procedures and surgeries.


![Basics of 2D codes VOL.1 [Types of 2D codes]](/img/asset/AS_151321_L.jpg)

