Filtering
The standards for filtering are still under review by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO). Given such circumstances, this section introduces the filtering methods under scrutiny and consideration for application to S-filter and L-filter.
Gaussian filter
The Gaussian filter is one kind of smoothing filter that suppress noise using the Gaussian function. Gaussian filters that are specified in JIS B 0632:2001 (ISO 11562:1996) and ISO 16610-21:2011 are analogously adopted to areal surface roughness measurement.
Spline filter
The spline filter is one kind of filter used to obtain a smooth profile by interpolating the sections between effective adjacent points using the spline function. Spline filters that are specified in ISO/TS 16610-22:2006 are analogously adopted to areal surface roughness measurement.
S-filter and L-filter settings
Cutoff wavelength for S-filter
A value equal to or more than 3 times the measurement resolution for the XY plane (horizontal plane) is used. If the set value is not sufficiently effective, increase the set value until the scale-limited surface noise is removed. If a different kind of filtering was applied beforehand, this may not be used.
Cutoff wavelength for L-filter
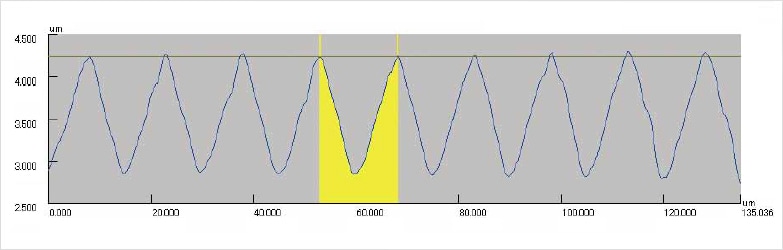
The cutoff wavelength for L-filter is difficult to uniformly specify based on lens magnification or stylus tip diameter; therefore, it must be adjusted with reference to the real surface. Set a value 5 times the XY-directional length of the profile that you wish to remove as waviness.
Example:
| Profile 1 |
Horizontal distance |
| Section 1 |
14.678 μm |
In the example above, the cutoff value is 0.1 mm.
14.678 x 5 = 73.39 ≈ 0.1 mm


