Surface Roughness Terminology
This section explains the terms used in ISO 25178 Surface Texture.
| Angular spectrum (graph) | The angular spectrum indicates a graph for determining the direction of the lay (or surface pattern; hairline, in the case of metal) comprising a surface. |
|---|---|
| Auto-correlation function | Auto-correlation function is used to evaluate the periodicity of surface roughness in the direction of the plane. |
| Course line | Curve separating adjacent hills |
| Dale | Region around a pit such that all maximal downward paths end at the pit |
| Definition area | Definition area is the portion of the evaluation area that is used for parameter definition. |
| Evaluation area | Evaluation area is the portion of the scale-limited surface that is subject to evaluation. |
| F-operator | F-operator removes form from the primary surface. This filter is equivalent to tilt correction, suppressing the nominal surface texture characterisation. |
| Height | The height represents the distance between the reference surface and each point on the scale-limited surface. A point lower than the reference plane has a negative value. |
| Hill | Region around a peak such that all maximal upward paths end at the peak |
| L-filter | L-filter is a filter eliminating the largest scale elements from the surface (high-pass filter). This filter is used to remove undulation and other lateral components from the surface, and thus allows for the extraction of only the roughness components. L-filter is equivalent to the cutoff value λc in JIS B 0633-2001. |
| Local peak height | Height difference between the peak and its nearest saddle point connected by ridge line |
| Local pit height | Height difference between the pit and its nearest saddle point connected by course line |
| Peak | Point on the surface that is higher than all other points within a neighborhood of that point |
| Pit | Point on the surface that is lower than all other points within a neighborhood of that point |
| Primary surface | Primary surface is the surface obtained after S-filtering the real surface. |
| Real surface | Real surface indicates the surface constituted from measurement data in the XY plane direction. Generally, the height data is the subject of processing. |
| Reference surface | Reference surface is the base for the scale-limited surface, and represents the plane at the mean height of the evaluation area as per the ISO 25178 Surface Texture function. |
| Ridge line | Curve separating adjacent dales |
| S-filter | S-filter is a filter eliminating the smallest scale elements from the surface (low-pass filter). This filter is equivalent to the cutoff value λs in JIS B 0601-2001. In the case of contact-type surface roughness measurement, noise attributable to edge shapes is removed. |
| S-F surface | Surface filter is a surface obtained after applying an F-operator to the primary surface. |
| S-L surface | S-L surface is a surface obtained after applying an L-filter to the S-F surface. |
| Saddle point | Point at which the ridge lines and course line cross |
| Scale-limited surface | Scale-limited surface means either the S-F surface or the S-L surface. It is the equivalent of the roughness profile or waviness profile in the profile method. |
| Surface filter | Surface filter is a filtration operator applied to a surface. |
Segmentation
Watershed algorithm
The watershed algorithm is employed to partition regions, which are used in the calculation of feature parameters.
Water is poured into the surface landscape, and it runs along the surface shape and reaches the pit. Upon continuing to pour water, the water surfaces of water filling different pits make contact with each other. The set of these contact points is the ridge line that partitions the dale region. The same approach can be applied to the hill region by vertically inverting the process.
Wolf pruning
Peaks and pits merely need to be higher or lower that other points in their respective neighborhoods. For this reason,
a surface with fine asperity can have a vast number of peaks and pits. Applying the watershed algorithm to such surfaces can result in meticulous segmentation into minute hill and dale regions. In order to suppress this over-segmentation, the Wolf pruning method is used to remove regions below a certain height/depth threshold.
The threshold is provided as a percentage of the maximum height (Sz) of the surface. The default value is 5%.

Closed area, Open area
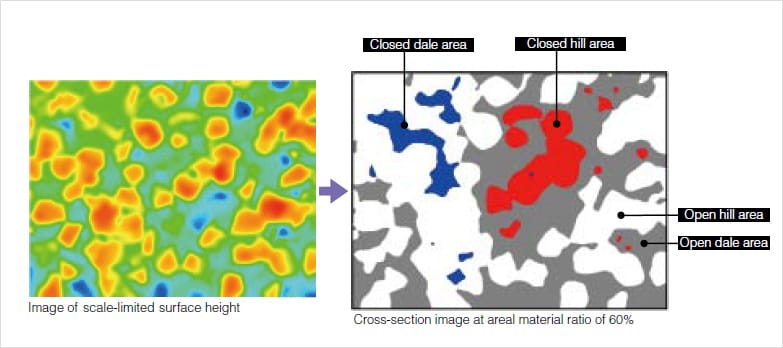
A region that is in contact with the boundary of the definition area at the material height c is called an "open area," while a region that is not is called a "closed area." Height c is given in areal material ratio and the default value is 50%.
